Introduction:
Gallstones are a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. These small, pebble-like deposits can form in the gallbladder and cause a range of uncomfortable and sometimes severe symptoms. In this blog, we will explore the basics of gallstones, including their causes, symptoms, and how they are diagnosed.
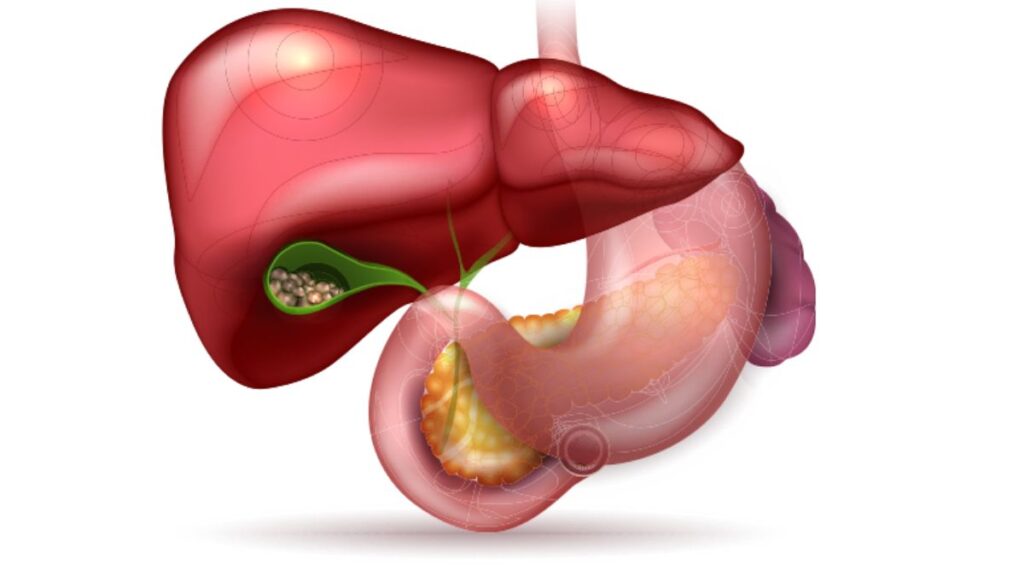
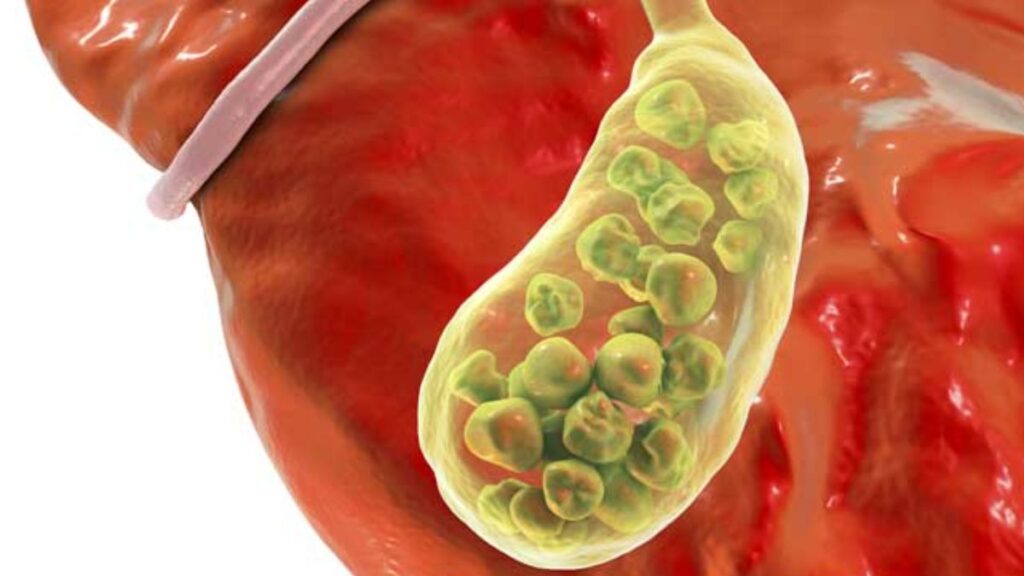
What Are Gallstones?
Gallstones, as the name suggests, are solid particles or stones that develop in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. The gallbladder plays a crucial role in the digestion process by storing bile produced by the liver. Bile is released into the small intestine to help digest fats. When the components of bile—cholesterol, bilirubin, and bile salts—become imbalanced, gallstones can form.
Causes of Gallstones:
Several factors contribute to the formation of gallstones. These include:
- Excess Cholesterol: When the bile in the gallbladder contains too much cholesterol, it can crystallize and form stones.
- Bilirubin Imbalance: High levels of bilirubin in the bile can lead to the formation of pigment gallstones.
- Gallbladder Dysfunction: A gallbladder that doesn’t empty properly can contribute to stone formation.
- Genetics: A family history of gallstones can increase the risk.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can raise the risk of developing gallstones.
- Rapid Weight Loss: Losing weight too quickly can increase the risk of gallstones.
Symptoms of Gallstones:
Gallstones don’t always cause symptoms, but when they do, the results can be painful and distressing. Common symptoms include:
- Intense Abdominal Pain: Often occurring in the upper right part of the abdomen, this pain can be excruciating and last for hours.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Gallstone pain can lead to nausea and vomiting.
- Back Pain Between Shoulder Blades: Pain may radiate to the back or between the shoulder blades.
- Bloating and Indigestion: Some people experience bloating and discomfort after eating, especially fatty foods.
- Jaundice: If a gallstone blocks the bile duct, it can lead to yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing gallstones typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests:
- Medical History: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, diet, and medical history.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination may reveal tenderness in the abdomen.
- Ultrasound: The most common test for detecting gallstones, ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the gallbladder.
- CT Scan or MRI: In some cases, these imaging tests may be necessary for a clearer view.
- Blood Tests: Elevated liver enzyme levels can indicate a blocked bile duct.
Conclusion:
Gallstones are a common medical issue, and understanding their causes, symptoms, and diagnosis is essential for early detection and appropriate treatment. If you suspect you may have gallstones or are experiencing symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. In future blog posts, we will explore treatment options and prevention strategies for gallstones to help you maintain optimal digestive health.