Introduction
The thyroid gland may be small, but it wields tremendous influence over our health, particularly in women. Understanding the intricate relationship between thyroid disease and women’s health is crucial, as thyroid disorders are more prevalent in females. In this blog, we’ll explore the impact of thyroid disease, its common types, symptoms, and the vital role it plays in women’s overall well-being.
The Thyroid’s Vital Role
Nestled in the front of your neck, the butterfly-shaped thyroid gland is a powerhouse that regulates various bodily functions. One of its primary duties is to produce hormones (T3 and T4) that control metabolism, impacting everything from body temperature to energy levels.
Types of Thyroid Disorders
There are two primary types of thyroid disorders:
Hypothyroidism: This occurs when the thyroid gland is underactive and produces insufficient hormones. It’s more common in women and can lead to symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and depression.
Hyperthyroidism: This is the opposite, where the thyroid gland is overactive, producing excessive hormones. It can cause symptoms such as anxiety, rapid heart rate, and weight loss.
Thyroid Disease and Women’s Health
Thyroid disorders, especially hypothyroidism, have a profound impact on women’s health:
- Fertility: An underactive thyroid can disrupt menstrual cycles and make it challenging to conceive. It’s vital for women planning to start a family to have their thyroid function evaluated.
- Pregnancy: Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in the development of the baby’s brain and nervous system. Untreated thyroid disorders during pregnancy can lead to complications, making regular thyroid testing essential.
- Menopause: Thyroid issues can exacerbate menopausal symptoms, like weight gain and mood swings. Addressing thyroid health can improve the overall menopausal experience.
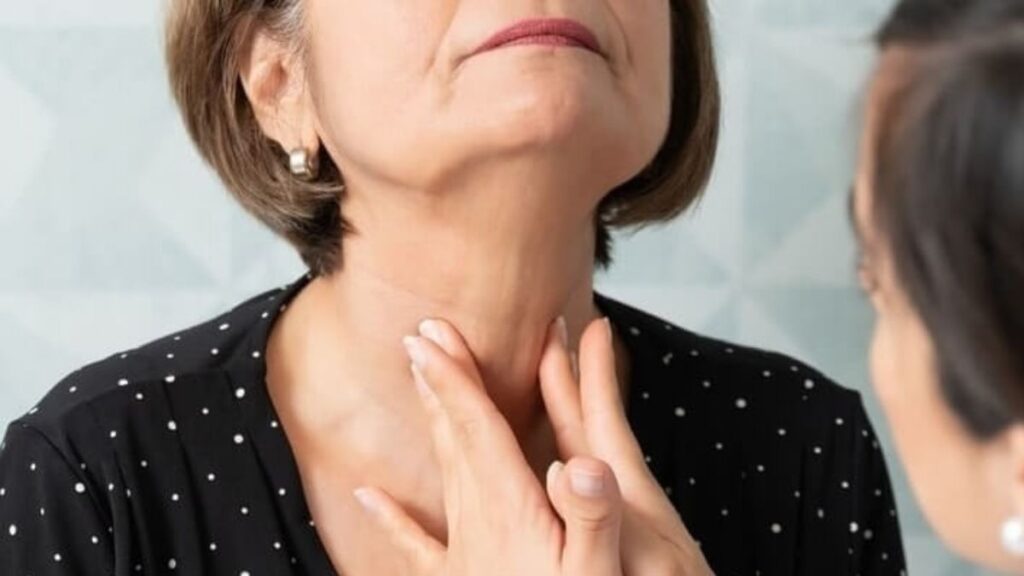
Symptoms of Thyroid Disease
Recognizing the signs of thyroid disorders is vital for early intervention:
Hypothyroidism Symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Hair loss
- Dry skin
- Depression
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Anxiety
- Weight loss
- Tremors
- Sweating
- Trouble sleeping
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels. Treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of the disorder. Medications like levothyroxine are common for hypothyroidism, while hyperthyroidism may require anti-thyroid drugs, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery.
Lifestyle Management
In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments can help manage thyroid disorders:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in iodine, selenium, and essential nutrients.
- Exercise regularly to support metabolism and overall health.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques and mindfulness.
- Ensure regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor thyroid function.
In conclusion, thyroid disease is a significant concern for women’s health. By understanding its impact and recognizing the symptoms, women can take proactive steps to maintain their thyroid health. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and early intervention are essential for managing thyroid disorders effectively and ensuring overall well-being.

