Introduction:
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it is often associated with adolescence, acne can occur at any age and can have a significant impact on a person’s self-esteem and overall well-being. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, types, and various treatment options available for managing acne.
Causes of Acne:
Acne develops when the hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. Several factors contribute to the development of acne, including hormonal changes, excessive oil production, certain medications, and genetic predisposition. Hormonal changes during puberty can lead to increased oil production, which can clog the pores and cause acne breakouts.
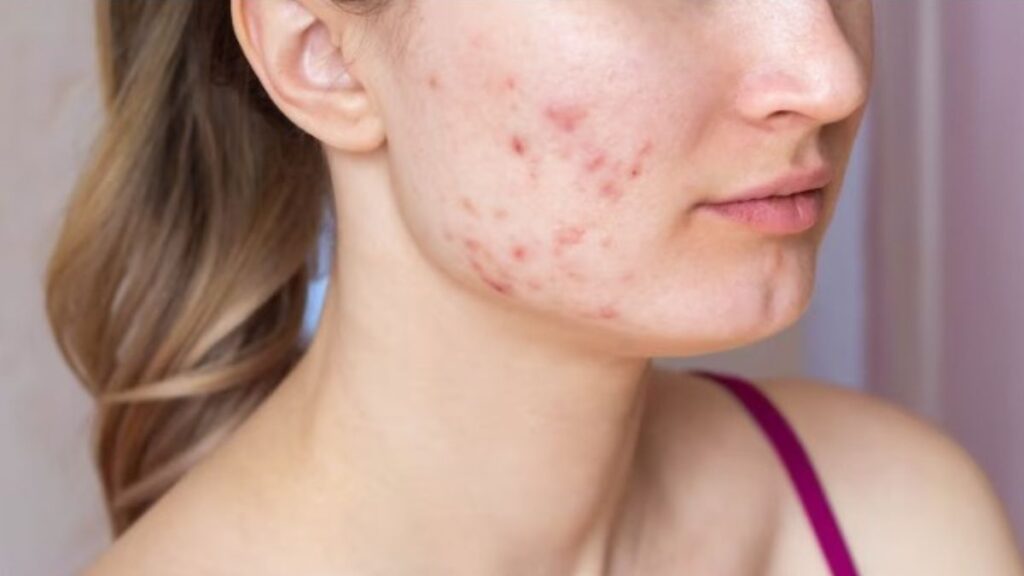

Types of Acne:
Acne can manifest in different forms, and understanding the different types can help in determining the most effective treatment approach. The most common types of acne include:
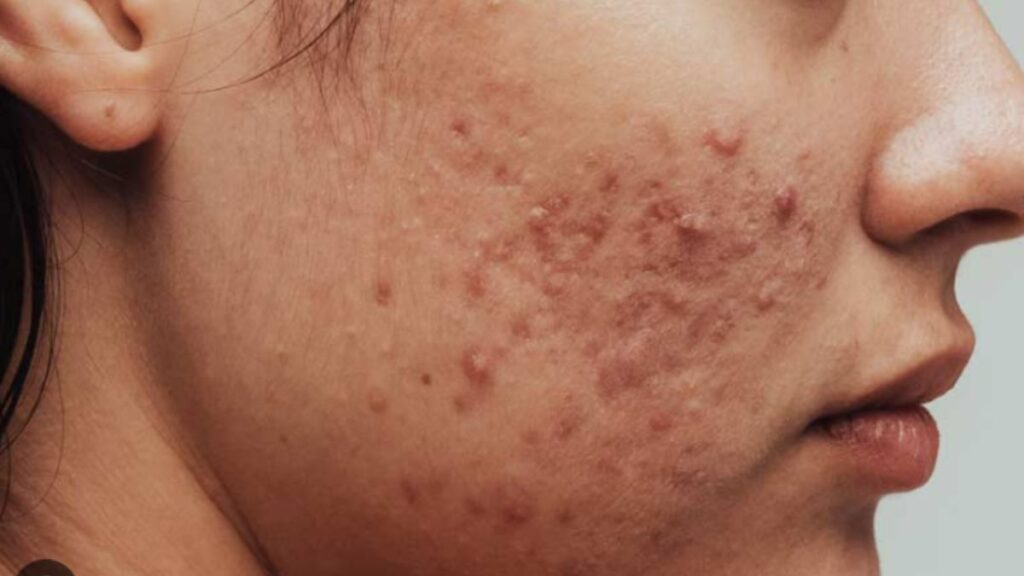
- Whiteheads and Blackheads: These are non-inflammatory acne lesions characterized by clogged pores. Whiteheads are closed comedones that appear as small, flesh-colored bumps, while blackheads are open comedones that have a darkened appearance due to oxidation.
- Papules and Pustules: These are inflammatory acne lesions that occur when the hair follicles become inflamed. Papules are small, red bumps, while pustules are similar but filled with pus, giving them a white or yellowish appearance.
- Nodules and Cysts: These are severe forms of acne that occur deep within the skin. Nodules are large, painful, solid bumps, while cysts are pus-filled, painful lesions. These types of acne can lead to scarring if not treated promptly.
Treatment Options:
Fortunately, there are various treatment options available to manage acne and improve the condition of the skin. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of acne, skin type, and individual preferences. Here are some common treatment options:
- Topical Medications: Over-the-counter creams, gels, and lotions containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids can help unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and kill bacteria.
- Oral Medications: In more severe cases, dermatologists may prescribe oral medications such as antibiotics, hormonal pills (for females), or isotretinoin (a powerful acne medication) to control acne.
- Professional Procedures: Dermatological procedures like chemical peels, microdermabrasion, laser therapy, or extraction of comedones can be effective in treating acne and improving the appearance of the skin.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also contribute to managing acne. Regularly washing the face with a gentle cleanser, avoiding excessive scrubbing, wearing non-comedogenic makeup, and keeping the skin moisturized can help prevent breakouts.
- Diet and Nutrition: While the relationship between diet and acne is still being studied, some evidence suggests that certain foods high in sugar, dairy products, or high-glycemic-index foods may exacerbate acne in some individuals. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is generally beneficial for overall skin health.
Conclusion:
Acne is a common and often distressing skin condition that can affect individuals of all ages. Understanding the causes, types, and available treatment options can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their acne. It is important to consult with a dermatologist to determine the most suitable treatment approach based on the severity and specific needs of each individual. With the right treatment and care, it is possible to effectively manage acne and achieve clearer, healthier skin.

