Introduction:
Childhood asthma is a prevalent chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of children worldwide. It can have a significant impact on a child’s quality of life, but with early recognition of symptoms and appropriate treatment strategies, children with asthma can lead active and fulfilling lives. In this blog, we’ll explore the early signs of childhood asthma and effective treatment approaches to ensure a healthier future for your child.
Recognizing Early Signs of Childhood Asthma:
Frequent Coughing: One of the most common early signs of childhood asthma is a persistent cough, especially at night or in the early morning. This cough may worsen during colds or respiratory infections.

Wheezing: Wheezing, a high-pitched whistling sound when breathing, can occur during exhalation in children with asthma. It often accompanies coughing.

Shortness of Breath: Children with asthma may experience difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity or exercise. This can lead to avoidance of sports or play.

Chest Tightness: Some children with asthma describe a sensation of tightness or discomfort in their chest. This symptom can be distressing and may prompt them to seek relief.

Frequent Respiratory Infections: Children with asthma may be more susceptible to respiratory infections, and these infections can exacerbate their asthma symptoms.

Effective Treatment Strategies for Childhood Asthma:
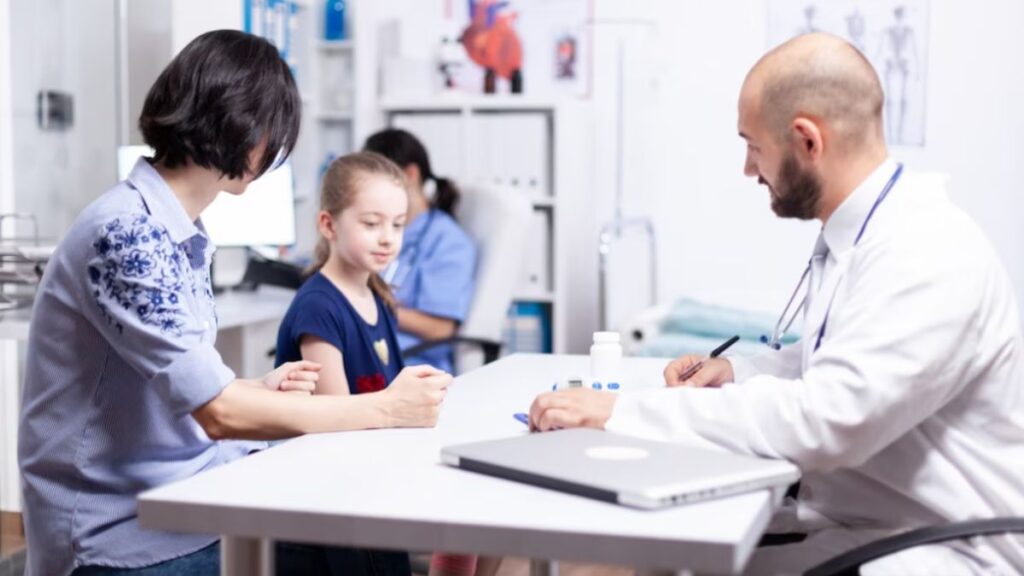
Consult a Pediatrician: If you suspect your child may have asthma or notice any of the early signs mentioned above, schedule an appointment with a pediatrician. They can perform tests, such as spirometry, to diagnose asthma and determine its severity.
Create an Asthma Action Plan: Work with your healthcare provider to create a personalized asthma action plan. This plan should outline your child’s asthma triggers, medications, and steps to take in case of an asthma attack.
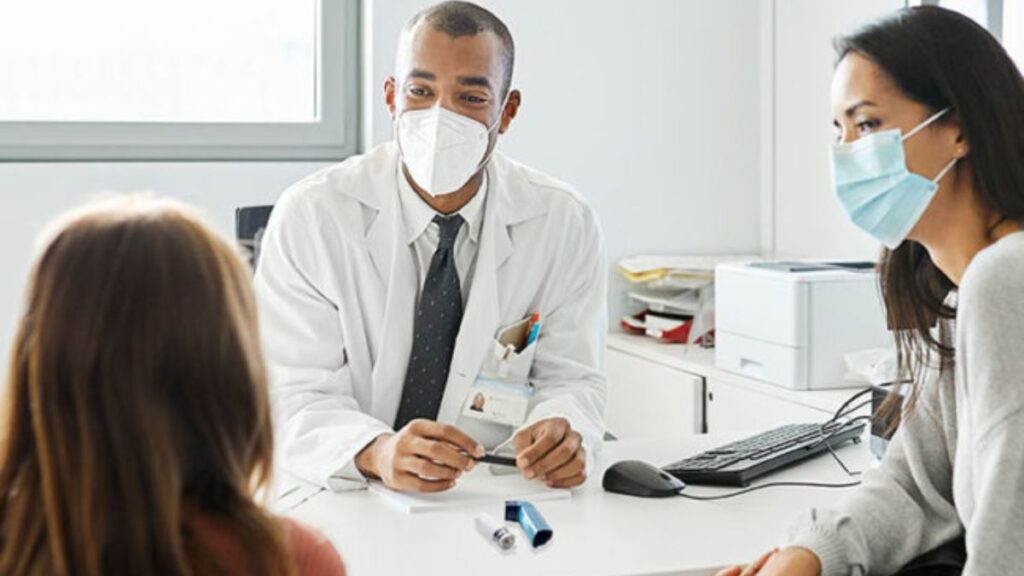

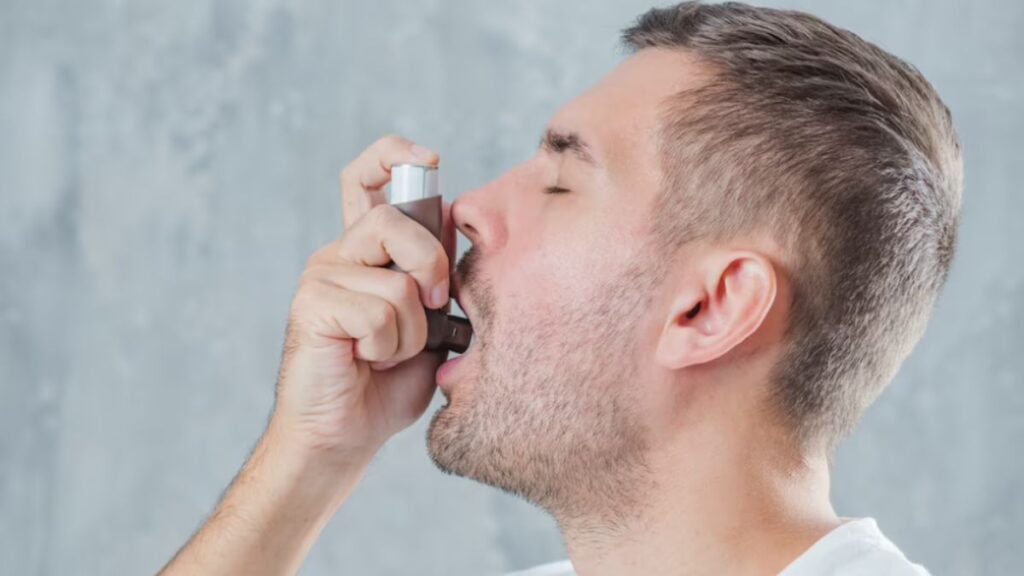
Medications: Asthma medications are typically categorized as relievers (for acute symptom relief) and controllers (to prevent symptoms). Common medications include bronchodilators (e.g., albuterol) and corticosteroids (e.g., inhaled or oral).

Inhaler Use: Ensure your child knows how to use their inhaler correctly. Proper technique is crucial for the medication to be effective. Younger children may use a spacer with their inhaler to make it easier.

Avoid Triggers: Identify and minimize exposure to asthma triggers, such as tobacco smoke, allergens (e.g., pollen, dust mites, pet dander), and respiratory infections.

Regular Follow-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your child’s healthcare provider to monitor their asthma and adjust treatment as needed. Asthma severity can change over time, so it’s essential to stay informed.

Promote Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Encourage your child to maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating well, staying physically active, and getting adequate sleep. These habits can help manage asthma symptoms.

Education and Support: Educate your child about their condition and involve them in managing their asthma. Support groups and educational resources can help both you and your child better understand asthma.

Conclusion:
Childhood asthma can be effectively managed with early recognition of symptoms and appropriate treatment strategies. By working closely with your child’s healthcare provider and following an asthma action plan, you can help your child enjoy a full and active life while minimizing the impact of asthma on their well-being. Stay vigilant for early signs, provide a supportive environment, and prioritize your child’s respiratory health to ensure a brighter, asthma-controlled future.











