Introduction:
When we think of chickenpox, we often associate it with childhood, but did you know that adults can also contract this highly contagious disease? While chickenpox in adults is less common than in children, it can be more severe and pose serious health risks. In this blog, we’ll explore what you need to know about chickenpox in adults, including its symptoms, complications, treatment, and prevention.
Chickenpox in Adults: Symptoms and Challenges:
Chickenpox in adults can be more challenging for several reasons. Firstly, the symptoms in adults are often more severe compared to children. Here are the primary symptoms of chickenpox in adults:
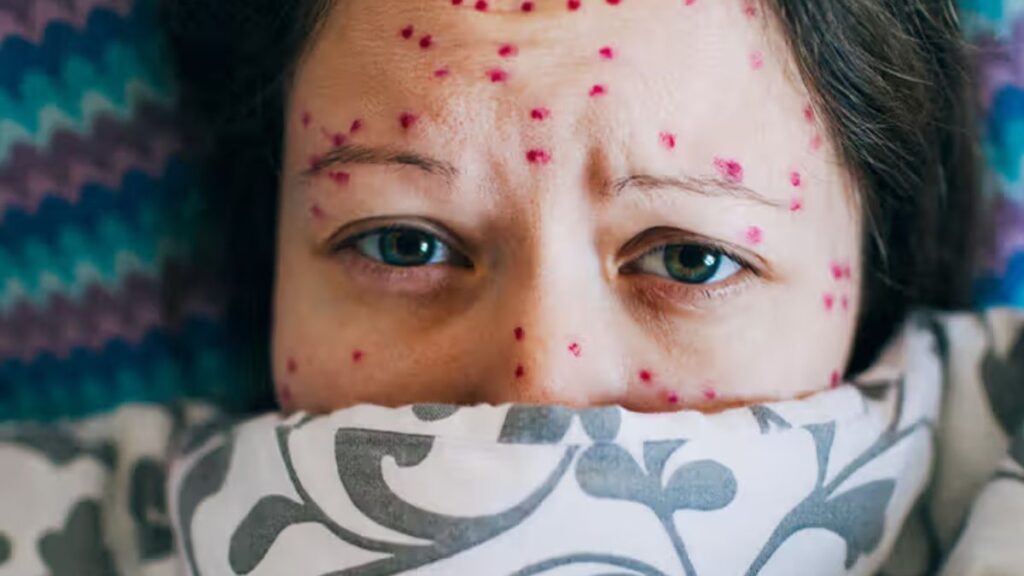
- Rash: Like in children, chickenpox in adults begins with a red, itchy rash that turns into blisters. The rash can cover a large portion of the body.
- Fever: Adults with chickenpox frequently experience a higher fever than children, which can lead to discomfort and complications.
- Headache and Body Aches: Headaches, body aches, and fatigue are common symptoms that can be more pronounced in adults.
- Respiratory Complications: Adults are more likely to develop complications affecting the respiratory system, such as pneumonia.
- Skin Infections: Scratching the blisters can lead to skin infections, scarring, and more severe discomfort in adults.
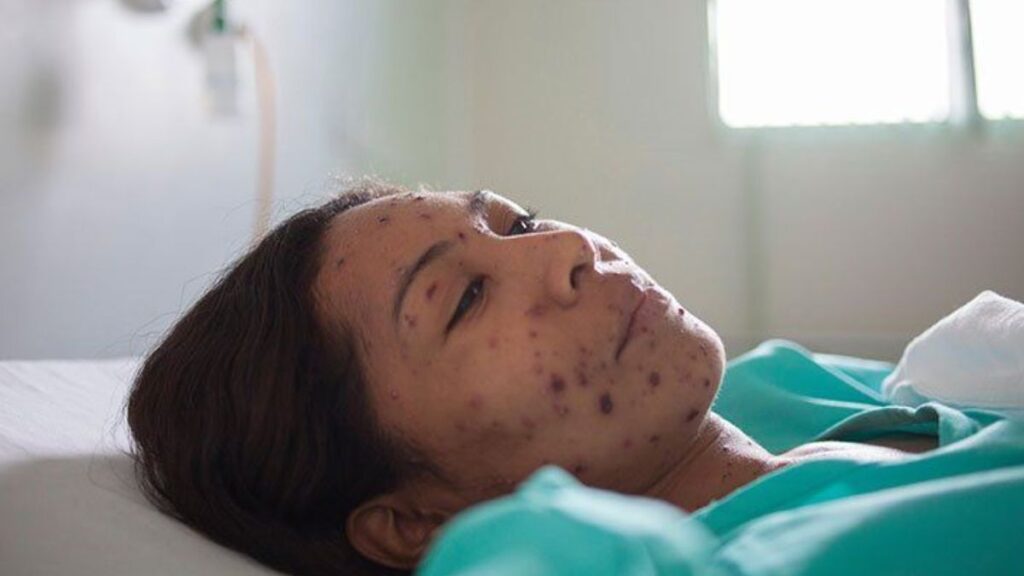
Complications and Risks:
Chickenpox can lead to various complications in adults, including:
- Pneumonia: Adults are at a higher risk of developing pneumonia as a complication of chickenpox, which can be severe and require hospitalization.
- Shingles (Herpes Zoster): Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which can remain dormant in the body. In some cases, it reactivates as shingles later in life.
- Encephalitis: While rare, chickenpox can lead to inflammation of the brain (encephalitis), which can be life-threatening.
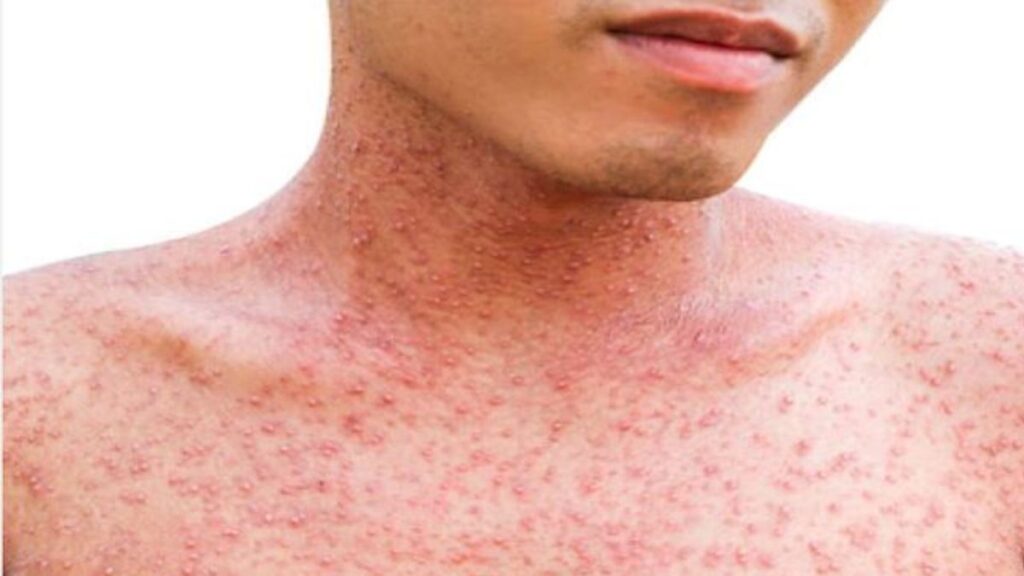
Treatment and Management:
If you suspect you have chickenpox as an adult, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. Treatment options may include:
- Antiviral Medications: Antiviral medications can help reduce the severity and duration of the illness if started early.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate discomfort and reduce fever.
- Antihistamines: These can help with itching and discomfort associated with the rash.
- Rest and Hydration: Getting plenty of rest and staying hydrated is essential for recovery.

Prevention Measures:
The best way to prevent chickenpox in adults is through vaccination. If you have never had chickenpox or been vaccinated, it’s a good idea to get the varicella vaccine. Additionally, if you have been in close contact with someone who has chickenpox, seek medical advice as vaccination or post-exposure prophylaxis may be recommended.
In conclusion, while chickenpox is often considered a childhood disease, it can affect adults with more severe symptoms and complications. Understanding the risks, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking prompt medical attention are crucial for managing chickenpox in adults. Vaccination remains the most effective way to prevent chickenpox and its potentially serious consequences in both children and adults.












