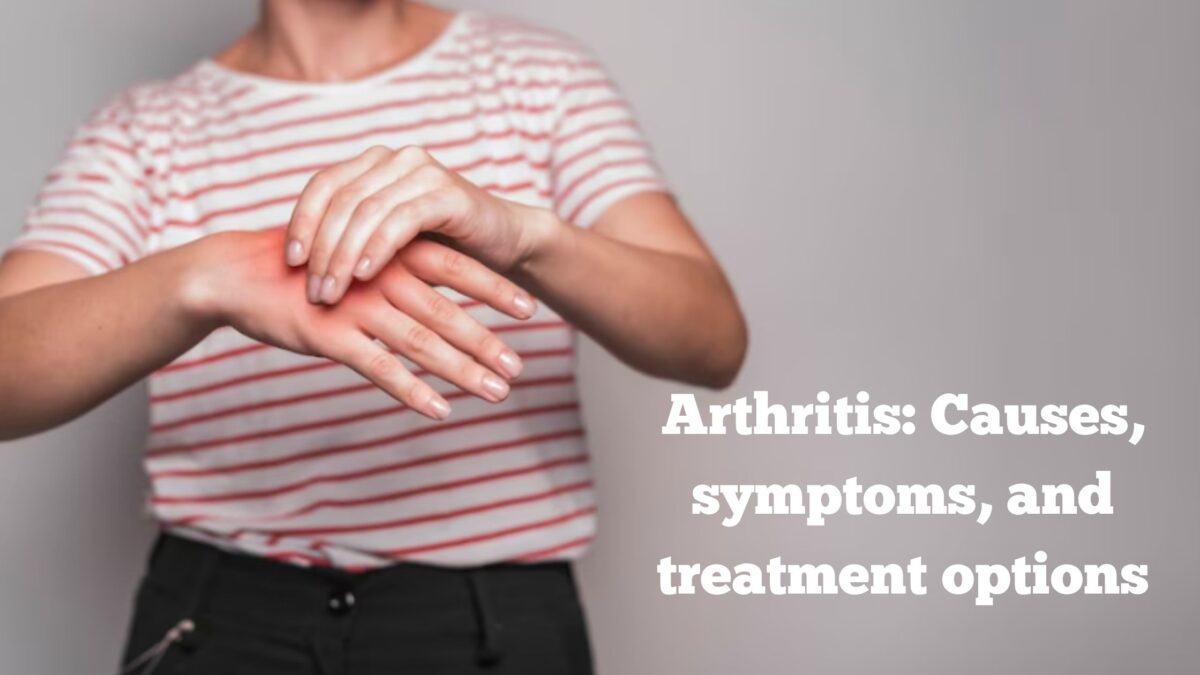
Arthritis is a term used to describe inflammation of one or more joints in the body. It affects people of all ages and can be a chronic condition that causes pain, stiffness, and swelling. In this blog, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for arthritis.
Causes of Arthritis:
Arthritis refers to a group of conditions that cause inflammation and stiffness in one or more joints of the body. There are many different types of arthritis, each with their own causes and risk factors. Here are some of the most common causes of arthritis:
Age:

As people get older, their joints tend to deteriorate and become less flexible. This can lead to the development of osteoarthritis, which is the most common type of arthritis in older adults.
Genetics:
Some types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can be inherited. If someone in your family has arthritis, you may be more likely to develop the condition yourself.
Injuries:
Joint injuries, such as fractures or dislocations, can increase the risk of developing arthritis later in life. This is because the injury can damage the cartilage that cushions the joint, leading to inflammation and eventually arthritis.
Infections:

Certain infections, such as Lyme disease or hepatitis C, can cause arthritis. In these cases, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, leading to inflammation and joint damage.
Autoimmune disorders:
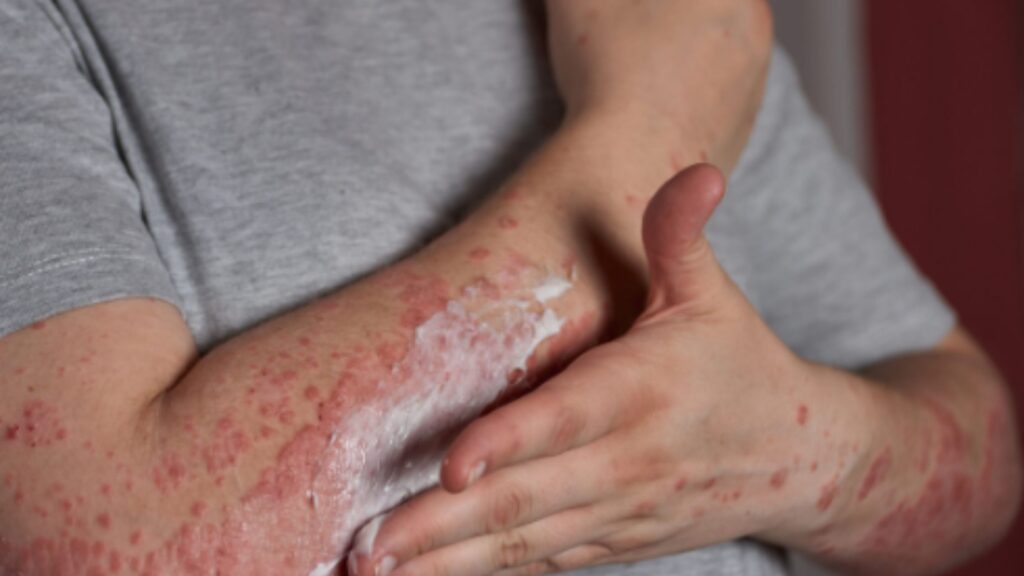
In autoimmune disorders, the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissues, including the joints. This can lead to the development of conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
Obesity:

Being overweight or obese can put extra stress on the joints, leading to inflammation and the development of arthritis.
It’s important to note that not everyone with these risk factors will develop arthritis, and not all cases of arthritis can be linked to a specific cause. However, by understanding these risk factors, you can take steps to reduce your risk of developing arthritis and manage your symptoms if you do develop the condition.
symptoms of Arthritis:
Here are some of the symptoms of arthritis:
- Pain: Pain in the affected joint is the most common symptom of arthritis. It can range from mild to severe and can be constant or intermittent. The pain may be described as a dull ache, burning sensation, or sharp stabbing pain.
- Stiffness: Stiffness is another common symptom of arthritis. It may be worse in the morning or after a period of inactivity. The joint may feel stiff and difficult to move, making it hard to perform daily activities.
- Swelling: Swelling is a common symptom of arthritis, particularly in RA. The affected joint may become swollen and inflamed, making it appear red and feel warm to the touch.
- Limited Range of Motion: Arthritis can cause a limited range of motion in the affected joint. You may find it difficult to bend or straighten your joint or to move it through its full range of motion.
- Fatigue: Fatigue is a common symptom of RA, as the body’s immune system attacks healthy cells, causing inflammation and fatigue.
- Weakness: Weakness in the affected joint is a common symptom of arthritis, particularly in RA. The joint may feel weak and unstable, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
- Deformity: Over time, arthritis can cause deformity in the affected joint, particularly in severe cases of OA or RA. This can lead to a loss of function in the joint, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent further joint damage.
Treatment options for Arthritis:
Here are some common treatment options for arthritis:
- Medications: There are a variety of medications that can be used to treat arthritis, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologics. These medications can help to reduce pain and inflammation, slow down joint damage, and improve overall function.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve joint flexibility, reduce pain, and increase strength. A physical therapist can design an individualized exercise program to help improve mobility and function.
- Occupational therapy: Occupational therapy can help people with arthritis to learn how to perform daily activities in a way that minimizes joint strain and pain. An occupational therapist can also recommend assistive devices, such as braces or splints, to help support and protect joints.
- Weight management: Excess weight can put extra strain on joints and exacerbate arthritis symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce pain and improve overall function.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat arthritis. Joint replacement surgery, such as hip or knee replacement, can be an effective option for people with severe joint damage.
- Alternative therapies: Some people find relief from arthritis symptoms through alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, or chiropractic care. However, it’s important to talk to a healthcare professional before starting any new therapy to ensure it’s safe and effective.
Overall, treatment options for arthritis are diverse and should be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and situation. Working with a healthcare professional can help to ensure that the most effective treatment plan is developed.