Introduction
Kidney stones are a common urological condition that affects both men and women. However, men are statistically more prone to developing kidney stones than women. In this blog, we’ll delve into the specifics of kidney stones in men, including the causes, symptoms, risk factors, prevention strategies, and treatment options.
Understanding Kidney Stones:
Kidney stones are solid, crystalline structures that form in the kidneys when certain substances in the urine become concentrated. These substances can include calcium, oxalate, uric acid, and cystine. When these substances accumulate, they can stick together and create a stone.
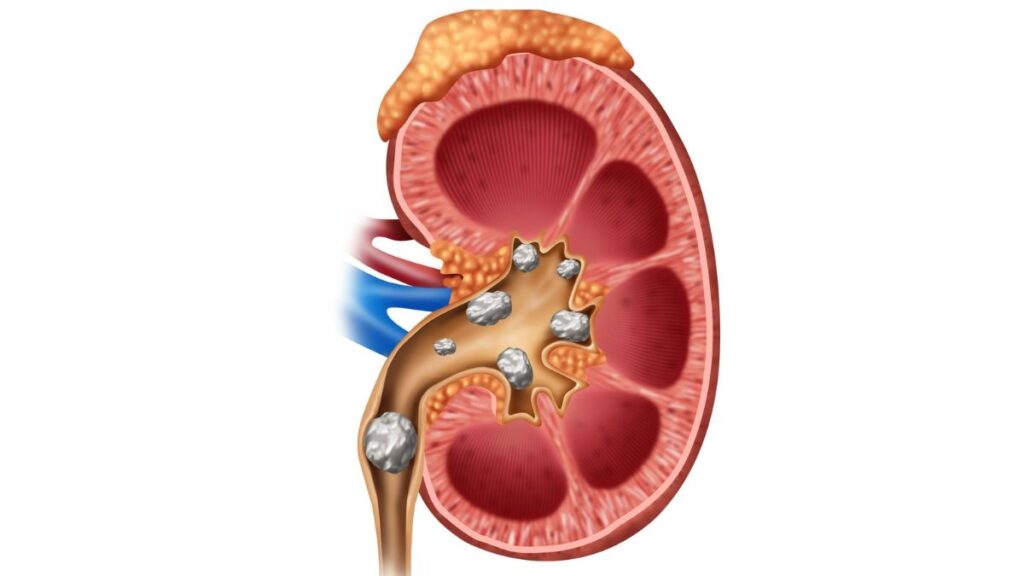
Causes of Kidney Stones in Men:
Several factors contribute to the development of kidney stones in men, including:
Dehydration: Inadequate fluid intake can lead to concentrated urine, increasing the likelihood of stone formation.

Diet: Consuming a diet high in sodium, animal protein, and oxalate-rich foods can raise the risk of stone formation.

Family History: A family history of kidney stones can increase the likelihood of developing them.

Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions like obesity, gout, and digestive diseases can contribute to stone formation.
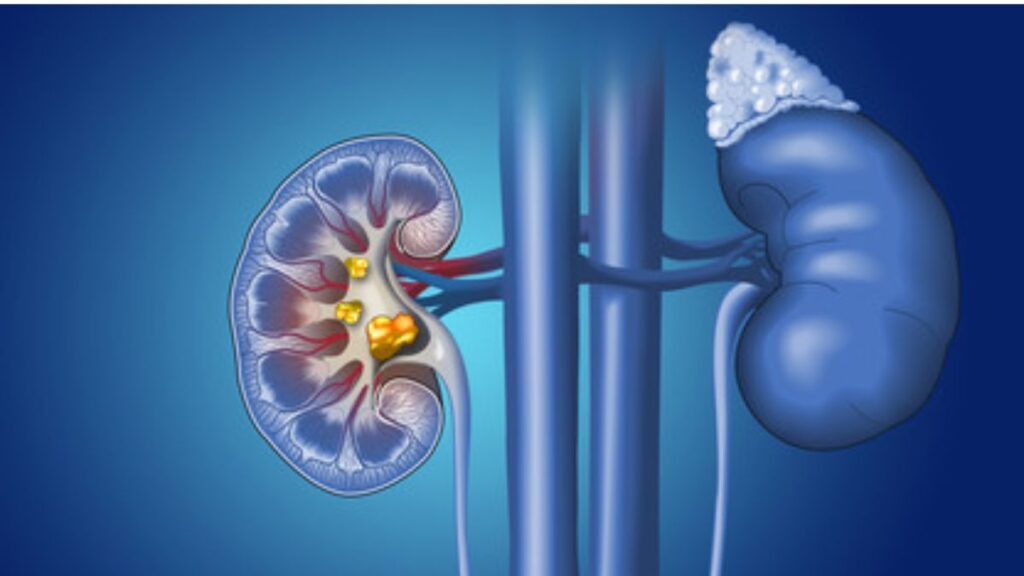
Medications: Some medications, like diuretics and antacids, can increase the risk of kidney stones.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones in Men:
Kidney stones can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Severe pain in the back, side, or lower abdomen: This is often described as one of the most intense pains a person can experience.
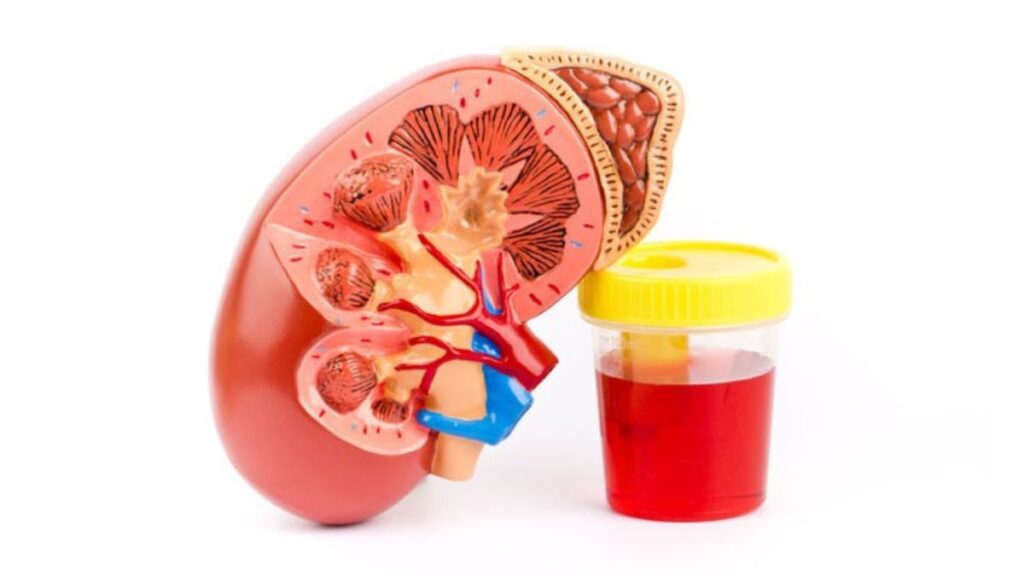
- Blood in the urine: Urine may appear pink, red, or brown.
- Frequent urination: Along with a persistent urge to urinate.

- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms may occur due to the pain.

Risk Factors:
In addition to the causes mentioned above, certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of kidney stones in men. These include being overweight or obese, having a sedentary lifestyle, and a history of previous kidney stones.
Prevention Strategies:
Preventing kidney stones is crucial, and the following strategies can help:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep urine diluted.

- Dietary Changes: Reduce sodium and limit animal protein and oxalate-rich foods.

- Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to prevent stone formation.
- Lifestyle Choices: Maintain a healthy weight and stay physically active.

Treatment Options:
If kidney stones do develop, treatment options may include:
- Medication: Depending on the type of stone, medication can help dissolve or pass the stone.
- Lithotripsy: Shock wave therapy can break the stone into smaller pieces for easier passage.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove or break up larger stones.
Conclusion:
Kidney stones can be extremely painful and disruptive, but they are manageable and preventable. If you’re a man with a history of kidney stones or at risk, taking proactive steps such as staying hydrated and making dietary changes can go a long way in reducing the likelihood of developing kidney stones. If you do experience symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention is essential for effective treatment and relief from the pain.












