Introduction:
Thyroid problems are increasingly common in today’s society, affecting millions of people worldwide. Despite their prevalence, thyroid disorders can be complex and often misunderstood. In this blog, we’ll delve into the intricacies of thyroid health, exploring the various types of thyroid problems, their symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Understanding the Thyroid:

The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, body temperature, and other essential bodily functions. It produces hormones—thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)—that influence nearly every cell in the body.
Types of Thyroid Problems:
Hypothyroidism:

This condition occurs when the thyroid gland fails to produce enough hormones, resulting in a slowdown of bodily processes. Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, sensitivity to cold, constipation, dry skin, and hair loss.
Hyperthyroidism:
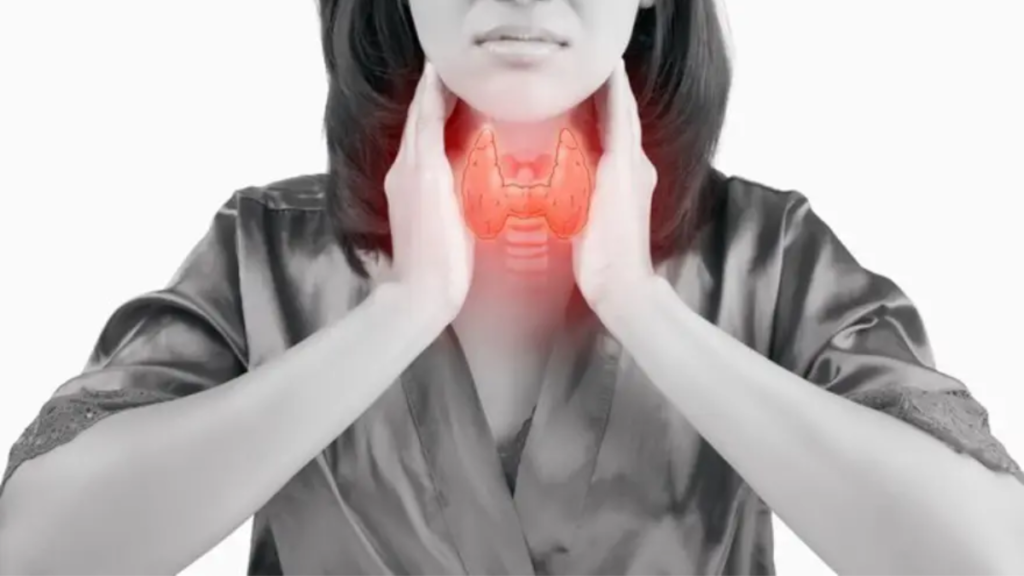

In contrast, hyperthyroidism is characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, leading to an excess production of thyroid hormones. Symptoms may include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, irritability, tremors, sweating, and heat intolerance.
Thyroid Nodules:

Thyroid nodules are growths or lumps that develop within the thyroid gland. While most nodules are benign, some may be cancerous. Symptoms can vary, but some people may experience difficulty swallowing, neck swelling, or hoarseness.
Thyroiditis:

Thyroiditis refers to inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can be caused by autoimmune conditions, viral infections, or other factors. Depending on the type of thyroiditis, symptoms may include neck pain, thyroid enlargement, fatigue, and hormonal imbalances.
Causes of Thyroid Problems:

The causes of thyroid disorders can vary depending on the specific condition. Hypothyroidism may be caused by autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, iodine deficiency, certain medications, or thyroid surgery. Hyperthyroidism can result from conditions such as Graves’ disease, thyroid nodules, or thyroiditis. Genetic factors, environmental triggers, and lifestyle choices may also contribute to thyroid dysfunction.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
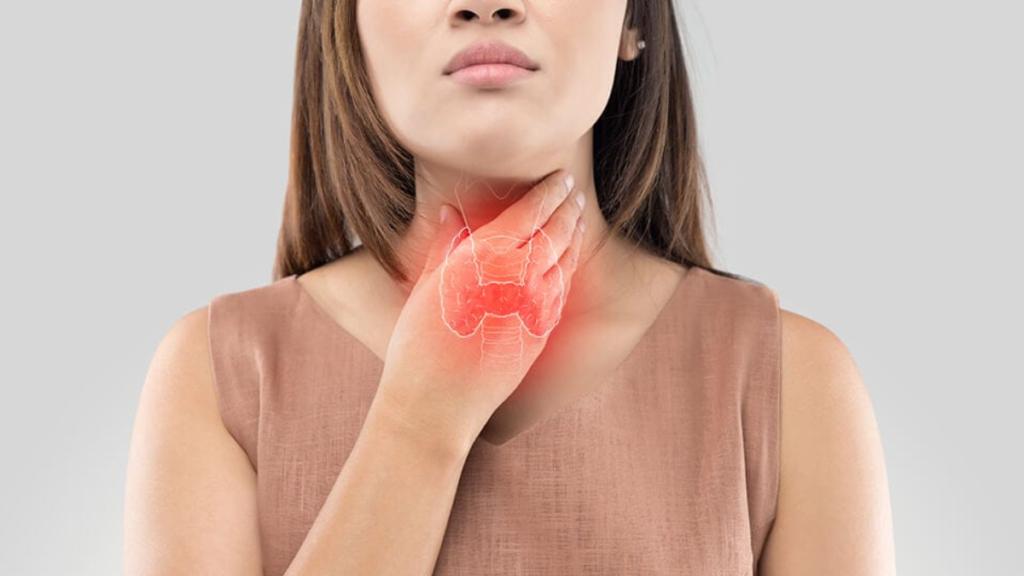

Diagnosing thyroid problems typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels, and imaging studies such as ultrasound or thyroid scans. Treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of the thyroid disorder.
Conclusion:
Thyroid problems are complex disorders that can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being. By understanding the different types of thyroid disorders, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their thyroid health effectively. Regular medical check-ups, monitoring thyroid function, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are essential for optimal thyroid health and overall wellness.