Introduction:
Orthopedic problems encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system, including bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. These issues can arise from various factors, such as injuries, overuse, aging, or underlying medical conditions. In this blog, we’ll delve into common orthopedic problems, their causes, symptoms, and available treatment options to help you better understand and manage these conditions.
Osteoarthritis:
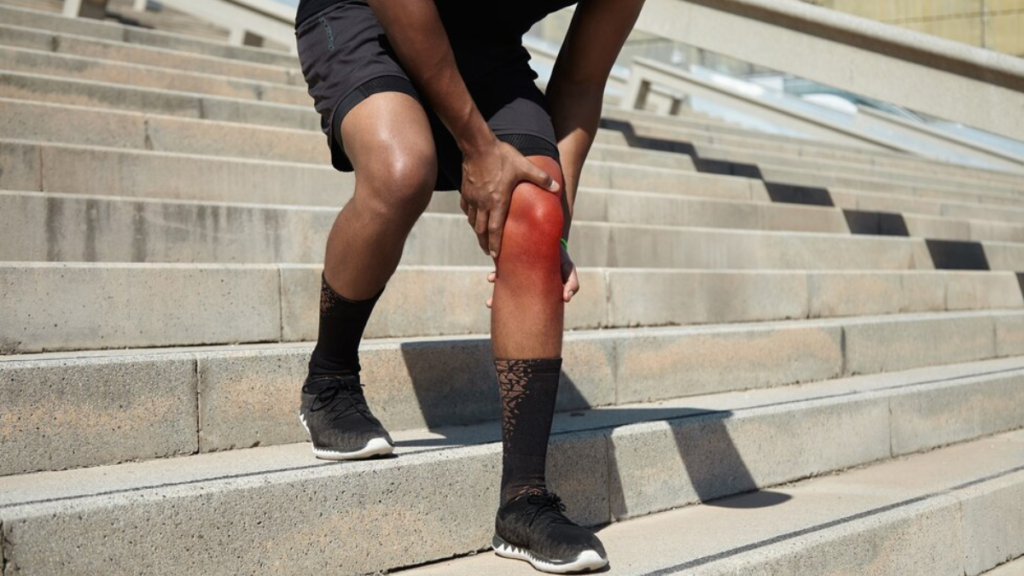

Osteoarthritis is the most prevalent form of arthritis, characterized by the degeneration of joint cartilage and underlying bone. It commonly affects weight-bearing joints like the knees, hips, and spine, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. Risk factors include age, obesity, joint injuries, and genetics. Treatment may include medication, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and in severe cases, joint replacement surgery.
Rheumatoid Arthritis:

Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium (lining of the joints), causing inflammation, pain, and joint damage. It can affect multiple joints symmetrically and may also involve other organs. Treatment aims to reduce inflammation, alleviate symptoms, and prevent joint damage through medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Fractures:
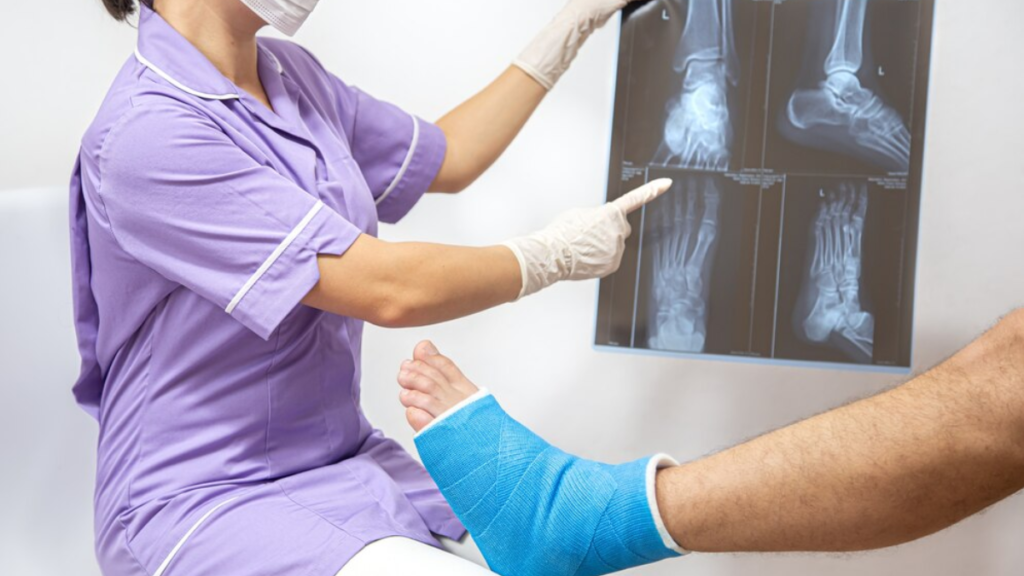
Fractures, or broken bones, can occur due to trauma, falls, sports injuries, or underlying bone weakness (osteoporosis). Symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, deformity, and difficulty moving the affected limb. Treatment varies depending on the type and severity of the fracture but may involve immobilization with casts or splints, realignment (reduction), and surgery for complex fractures.
Tendinitis:

Tendinitis refers to inflammation or irritation of a tendon, often resulting from repetitive movements, overuse, or sudden exertion. Common sites of tendinitis include the shoulder (rotator cuff tendinitis), elbow (tennis or golfer’s elbow), wrist (carpal tunnel syndrome), knee (patellar tendinitis), and Achilles tendon. Treatment typically involves rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications.
Sprains and Strains:
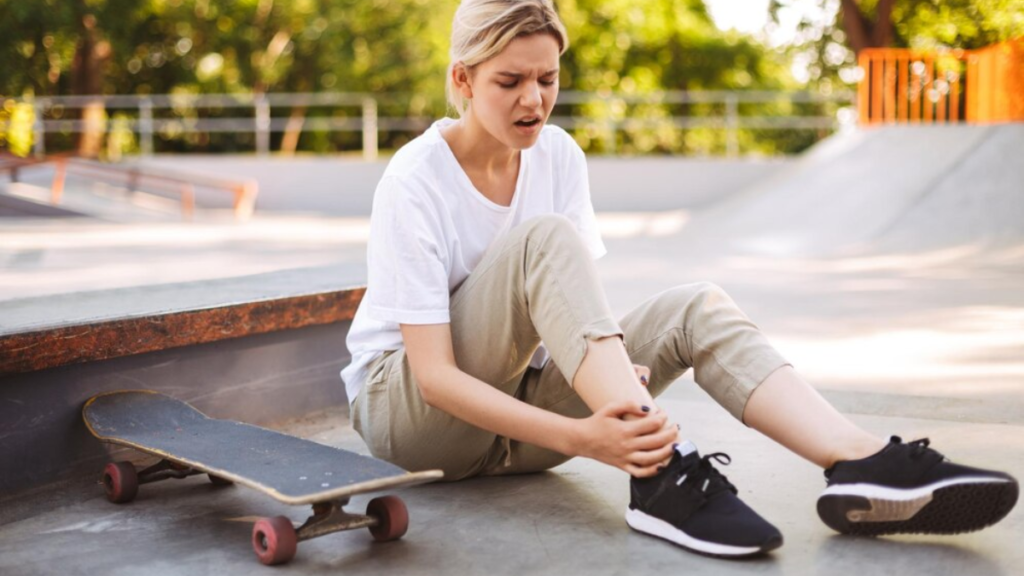

Sprains involve stretching or tearing of ligaments (connective tissue that connects bones), while strains affect muscles or tendons. These injuries commonly occur during sports, accidents, or sudden movements and present with pain, swelling, bruising, and limited mobility. Treatment includes rest, ice, compression, elevation, pain management, and rehabilitation exercises to restore strength and flexibility.
Herniated Disc:
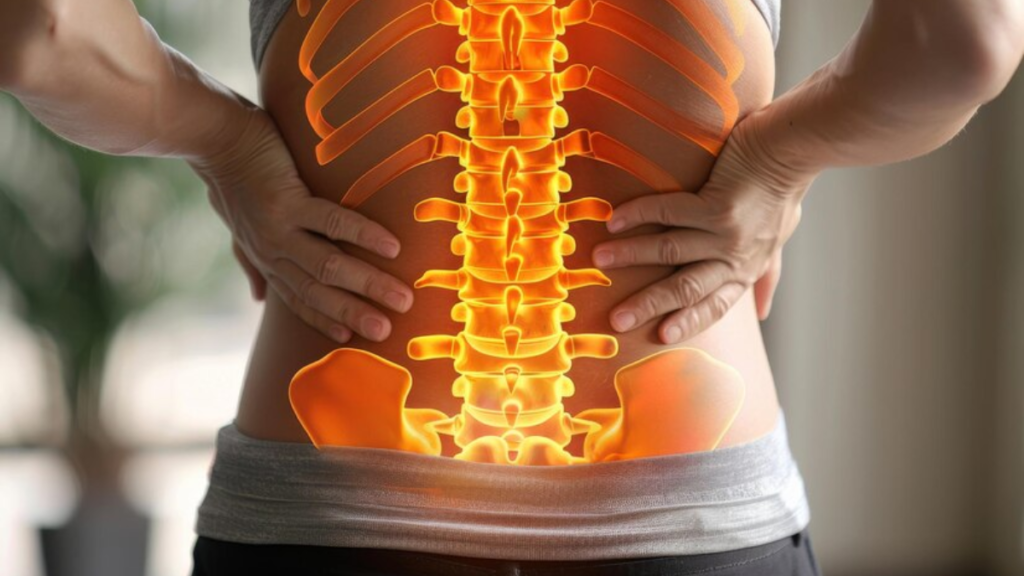
A herniated disc occurs when the soft, gel-like center (nucleus pulposus) of an intervertebral disc protrudes through the tough outer layer (annulus fibrosus), often due to wear and tear or sudden trauma. This can lead to nerve compression, causing back pain, sciatica (radiating leg pain), numbness, tingling, and weakness. Treatment options include rest, medication, physical therapy, spinal injections, and surgery for severe cases.
Conclusion:
Orthopedic problems can significantly impact quality of life, causing pain, disability, and limitations in daily activities. Early recognition of symptoms and prompt intervention are crucial for effective management and prevention of complications. If you’re experiencing persistent musculoskeletal symptoms, consult with an orthopedic specialist for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs. Remember, proactive care and lifestyle modifications can help alleviate symptoms and promote musculoskeletal health and well-being.