Stroke is a medical condition that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or reduced, causing brain cells to die. This can have a devastating impact on a person’s physical and cognitive abilities, and can even be life-threatening in some cases. In this blog post, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, and available treatments for stroke.
Symptoms of Stroke:
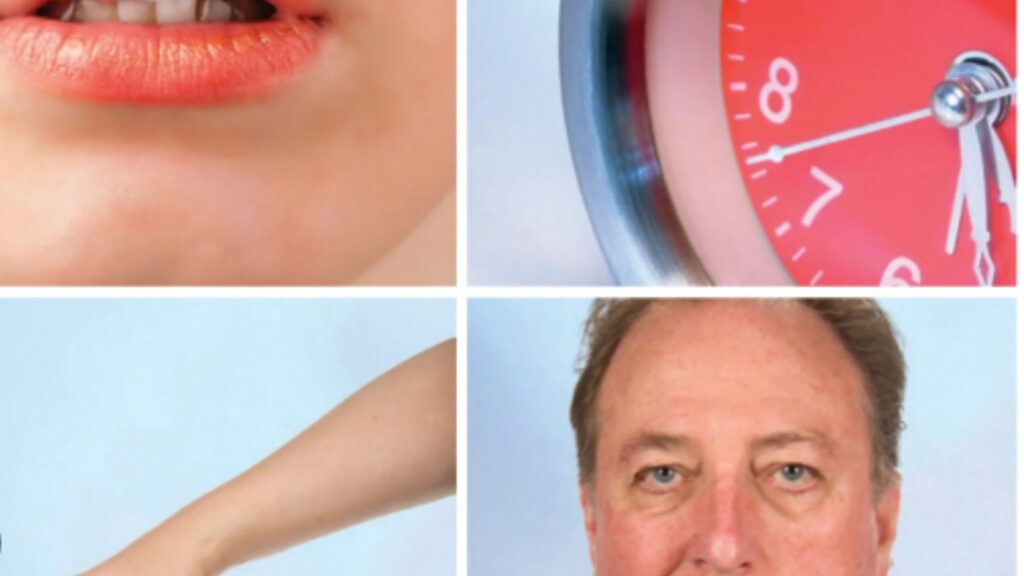
The symptoms of stroke can vary depending on the severity and location of the stroke. Some common symptoms include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body
- Sudden confusion, trouble speaking, or difficulty understanding others
- Sudden vision problems in one or both eyes
- Sudden dizziness, loss of balance, or difficulty walking
- Severe headache with no known cause
If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately, as early treatment can greatly improve the chances of recovery.
Causes of Stroke:

There are two main types of stroke: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel in the brain, cutting off the blood supply to a part of the brain. Hemorrhagic stroke, on the other hand, occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing bleeding in the brain.
Several risk factors can increase a person’s likelihood of having a stroke. Some common risk factors include:
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Family history of stroke
- Age (the risk of stroke increases with age)
By managing these risk factors, a person can reduce their likelihood of having a stroke.
Available Treatments for Stroke:
The treatment for stroke will depend on the type, severity, and location of the stroke. In general, the goal of treatment is to restore blood flow to the affected part of the brain as quickly as possible, in order to minimize brain damage.
Ischemic Stroke:
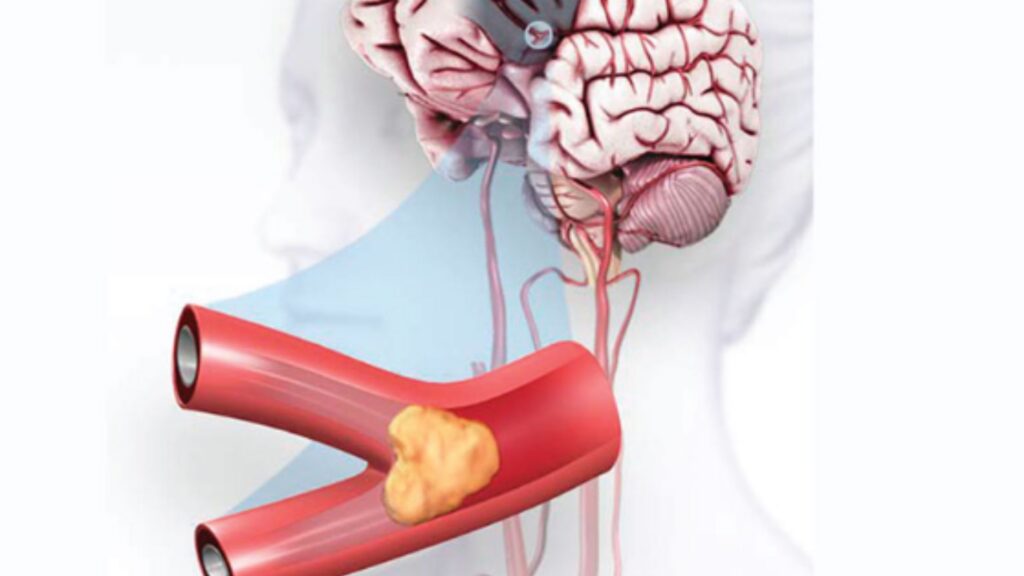
In the case of an ischemic stroke, the most common treatment is a medication called tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). This medication dissolves blood clots and restores blood flow to the affected area of the brain. However, tPA must be given within a few hours of the stroke in order to be effective, so it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
In some cases, a procedure called a mechanical thrombectomy may be performed. This involves using a catheter to remove the blood clot from the blocked blood vessel in the brain.
Hemorrhagic Stroke:
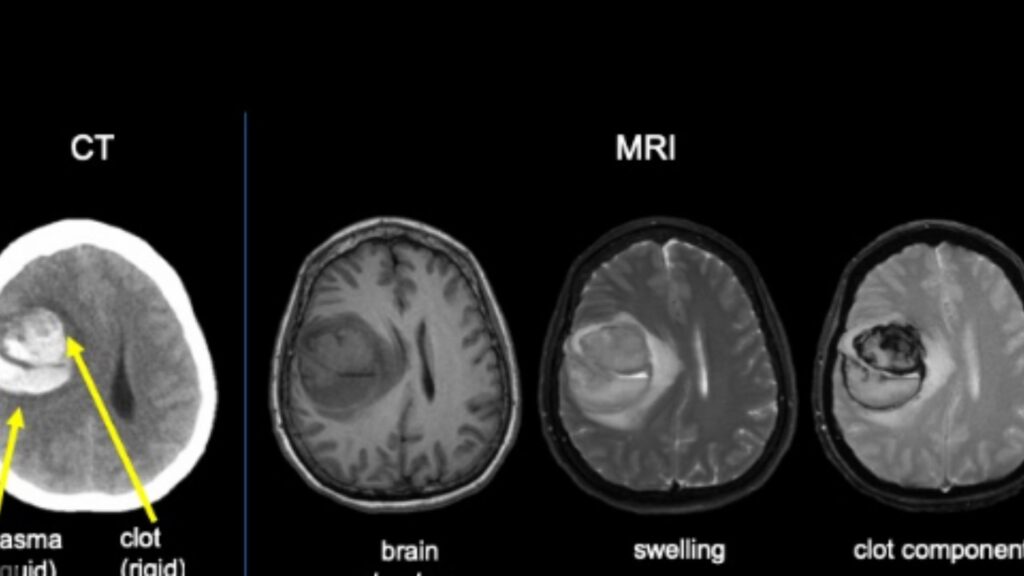
In the case of a hemorrhagic stroke, the goal of treatment is to stop the bleeding in the brain. This may involve surgery to remove the blood clot or repair the ruptured blood vessel.
In addition to these treatments, rehabilitation is often necessary after a stroke in order to help the patient regain their physical and cognitive abilities. This may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and other types of therapy as needed.
Conclusion:
Stroke is a serious medical condition that can have a devastating impact on a person’s life. However, by recognizing the symptoms and managing the risk factors, it is possible to reduce the likelihood of having a stroke. If a stroke does occur, early treatment is essential in order to minimize brain damage and improve the chances of recovery. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms of a stroke, seek medical attention immediately.











