Introduction
The human brain, an intricate web of neurons and glial cells, remains one of the most enigmatic and awe-inspiring organs in our body. However, this complexity also makes it susceptible to various health issues, including brain tumors. Unraveling the science behind brain tumors is crucial in our quest to combat these formidable adversaries. In this blog, we will delve into the mechanisms that give rise to brain tumors, explore the role of genetic mutations, and understand the intricate interplay of cellular processes that contribute to their development.
1.The Origin of Brain Tumors
To comprehend brain tumors, we must first understand the basic components of the brain. The brain comprises neurons, which are the cells responsible for transmitting signals, and glial cells, which provide support and protection to neurons. Brain tumors can develop from both neuron and glial cell types, giving rise to primary brain tumors.
The vast majority of brain tumors, approximately 80%, are gliomas—tumors that originate from glial cells. Among gliomas, glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) stands out as one of the most aggressive and deadly forms, characterized by its infiltrative nature and resistance to treatment.
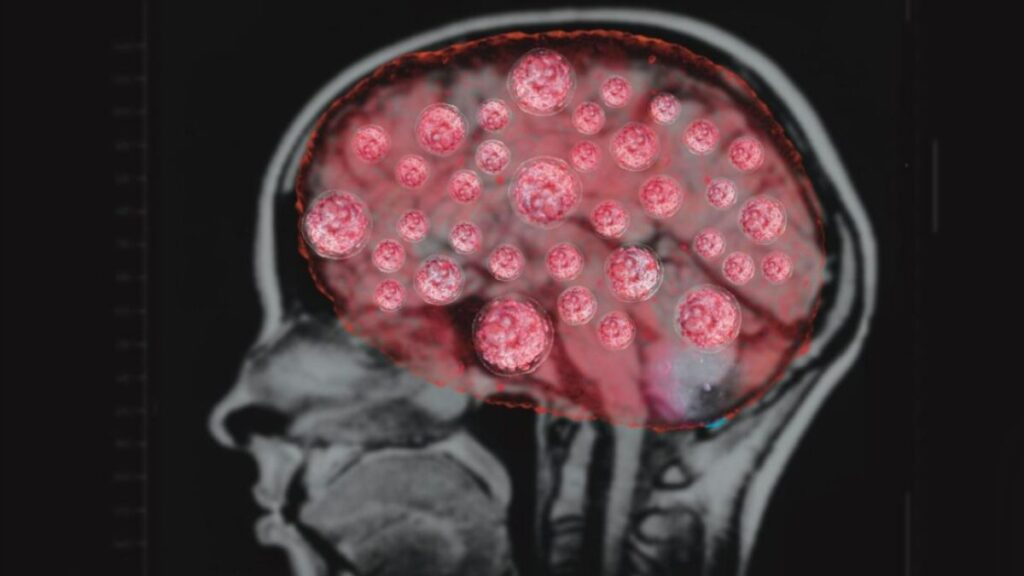
2.Genetic Mutations and Brain Tumors
Genetic mutations play a pivotal role in the development of brain tumors. Mutations can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, enabling tumor cells to evade normal regulatory mechanisms and proliferate rapidly. These mutations may arise spontaneously or be inherited from one’s parents.
In the case of glioblastomas, mutations in certain genes, such as the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene, play a significant role. EGFR mutations lead to the overexpression of EGFR protein, fueling the uncontrolled growth of tumor cells. Other genetic alterations, such as those involving the TP53 gene, contribute to the ability of tumor cells to evade cell death signals.
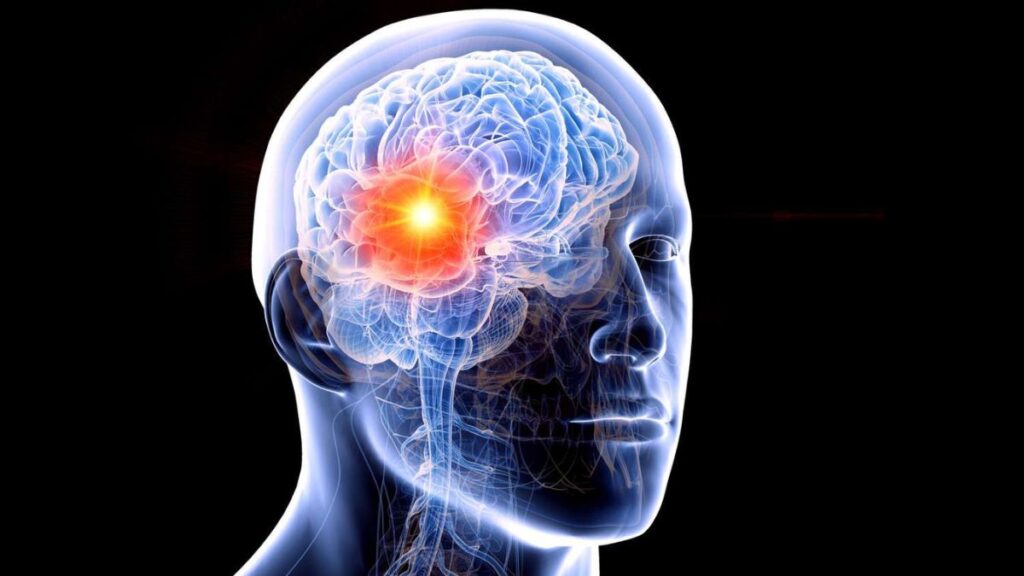
3.Cellular Processes and Tumor Development
Several complex cellular processes are involved in the development and progression of brain tumors. Two essential processes are angiogenesis and invasion:
a. Angiogenesis: As tumors grow, they require a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients to sustain their rapid expansion. To meet this demand, tumors stimulate the formation of new blood vessels through a process called angiogenesis. The new blood vessels provide the tumor with the necessary nourishment, facilitating its relentless growth.
b. Invasion: Gliomas, especially GBMs, are known for their invasive behavior. They send out tentacle-like projections that infiltrate neighboring brain tissue, making complete surgical removal nearly impossible. This invasive nature is a major challenge in treating brain tumors and contributes to their high recurrence rates.
4.Challenges in Brain Tumor Treatment
The complexity of brain tumors poses significant challenges for effective treatment. The blood-brain barrier, a protective mechanism that regulates the passage of substances from the bloodstream into the brain, limits the delivery of certain drugs to the tumor site. Additionally, the heterogeneous nature of brain tumors, with various cell types and genetic mutations coexisting within the same tumor, further complicates treatment strategies.

5.Advancements in Brain Tumor Research
Despite the challenges, advancements in brain tumor research offer hope for improved treatments. Targeted therapies, which aim to attack specific genetic mutations or cellular processes, are being developed to make treatments more effective and less harmful to healthy brain tissue. Immunotherapies, which harness the body’s immune system to recognize and attack tumor cells, show promise in clinical trials as well.

Conclusion
The science behind brain tumors is a complex and evolving field of study. Understanding the origin, genetic mutations, and cellular processes involved in brain tumor development is essential in our quest to find effective treatments and, ultimately, a cure. As researchers continue to unravel the enigma of brain tumors, collaboration between scientists, healthcare professionals, and patients remains crucial in our collective fight against this formidable adversary. With determination, innovation, and a deep understanding of the science at hand, we move closer to a future where brain tumors will no longer cast a shadow on the lives of those affected.