Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood due to the body’s inability to produce or use insulin effectively. Diabetes is a serious disease that can lead to a number of complications, including heart disease, stroke, nerve damage, kidney disease, and blindness. In this blog post, we will discuss the basics of diabetes, including its types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes:
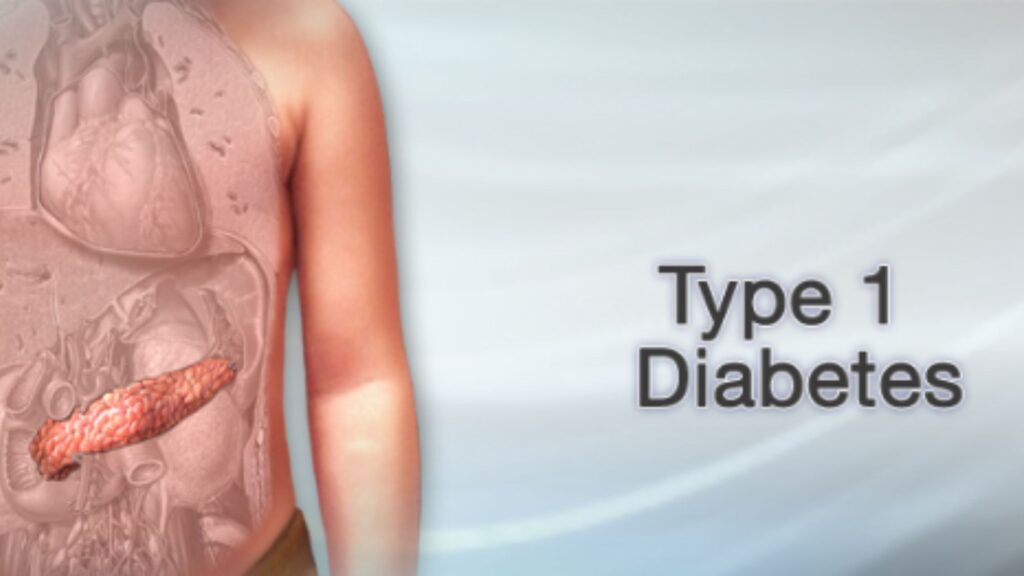
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This results in little or no insulin production, which means that the body is unable to use glucose for energy. Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in children and young adults, but it can occur at any age.
Type 2 diabetes:

Type 2 diabetes is a condition in which the body’s cells become resistant to insulin, or the body does not produce enough insulin to meet its needs. This type of diabetes is the most common form of the disease, and it typically develops in adults over the age of 40, although it can occur in younger individuals as well.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. It is usually diagnosed between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy and usually goes away after the baby is born. However, women who develop gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Causes of Diabetes:
The causes of diabetes are not fully understood, but several factors are thought to contribute to the development of the disease. These include:
Obesity:

Being overweight or obese is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Excess body fat can cause insulin resistance, which makes it harder for the body to use glucose for energy.
Poor diet:

A diet high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Sedentary lifestyle:
A lack of physical activity can also contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. Exercise helps to improve insulin sensitivity and can reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Genetics:
Type 1 diabetes is believed to have a strong genetic component, although the exact genes involved are not yet known. Type 2 diabetes is also believed to have a genetic component, but lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise play a larger role in its development
Symptoms of Diabetes:
The symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the type of diabetes and the severity of the condition. Some common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Frequent urination: High levels of glucose in the blood can cause the kidneys to work harder to filter out the excess sugar, which can result in frequent urination.
- Increased thirst: Excessive urination can lead to dehydration, which can cause increased thirst.
- Fatigue: The body’s inability to use glucose for energy can result in feelings of fatigue and lethargy.
- Blurred vision: High levels of glucose in the blood can cause the lens of the eye to swell, resulting in blurred vision.
- Slow healing: High levels of glucose in the blood can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds, which can lead to slow healing.
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet: High levels of glucose in the blood can damage nerves, which can cause numbness or tingling in the hands or feet.
Treatment Options for Diabetes:
While there is no cure for diabetes, there are various treatment options available that can help manage the condition and prevent complications.
- Insulin Therapy: Insulin therapy is the most common treatment for Type 1 diabetes, and it is often used for people with Type 2 diabetes who cannot manage their blood sugar levels through other means. Insulin is administered through injections or an insulin pump and helps to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Oral Medications: For people with Type 2 diabetes, oral medications may be prescribed to help lower blood sugar levels. These medications work by either increasing insulin production or improving insulin sensitivity.
- Lifestyle Changes: Making lifestyle changes such as losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and increasing physical activity can also help manage diabetes. Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels, while a healthy diet can help control weight and regulate blood sugar levels.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Continuous glucose monitoring involves wearing a small sensor that tracks blood sugar levels throughout the day. This can help people with diabetes monitor their blood sugar levels and adjust their insulin therapy or medication as needed.
- Pancreas Transplant: In some cases, a pancreas transplant may be an option for people with Type 1 diabetes who are unable to manage their blood sugar levels with insulin therapy.
- Bariatric Surgery: Bariatric surgery, also known as weight loss surgery, may be recommended for people with Type 2 diabetes who are severely overweight. This surgery can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
In conclusion, diabetes is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management to prevent complications. Treatment options range from insulin therapy and oral medications to lifestyle changes, continuous glucose monitoring, pancreas transplant, and bariatric surgery. Consultation with a healthcare provider is important to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for an individual’s specific needs.