Introduction
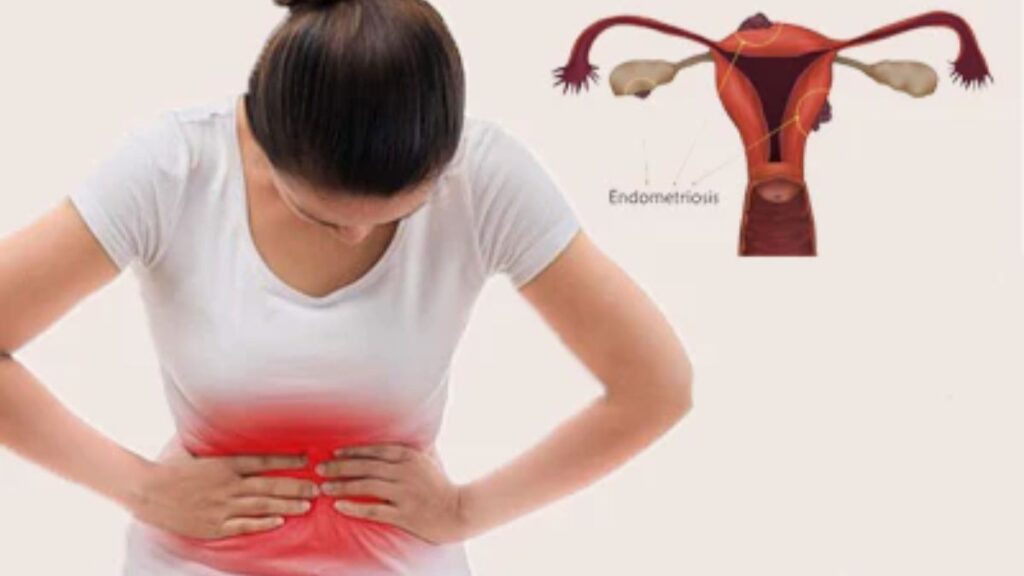
Endometriosis is a gynecological disorder that affects millions of women worldwide. This condition occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus, causing a range of symptoms and potential complications. In this blog post, we will delve into the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for endometriosis to help you better understand and manage this condition.
Symptoms of Endometriosis
Endometriosis can manifest in various ways, and its symptoms can vary in severity. Some common signs and symptoms of endometriosis include:
- Pelvic Pain: The most prevalent symptom is often chronic pelvic pain, which may worsen during menstruation.
- Painful Periods (Dysmenorrhea): Women with endometriosis frequently experience severe menstrual cramps that may disrupt daily activities.
- Painful Intercourse (Dyspareunia): Pain during or after sexual intercourse is another common symptom of endometriosis.
- Painful Bowel Movements or Urination: Endometrial tissue can grow on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or other pelvic organs, leading to pain during bowel movements or urination, especially during menstruation.
- Excessive Menstrual Bleeding: Some women with endometriosis may have heavier or longer menstrual periods than usual.
- Infertility: Endometriosis can affect fertility by blocking or damaging the fallopian tubes or by causing inflammation that hampers the implantation of a fertilized egg.

Diagnosis of Endometriosis
Diagnosing endometriosis often involves a combination of medical history, symptom evaluation, and medical tests. The following diagnostic steps are commonly used:
- Clinical Evaluation: Your healthcare provider will discuss your symptoms, medical history, and perform a physical examination.
- Pelvic Exam: A pelvic exam may help identify abnormalities such as cysts or scars.
- Imaging: Ultrasound or MRI scans can provide images of the pelvic region and may help detect endometrial growths.
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive surgical procedure called laparoscopy is the most definitive way to diagnose endometriosis. During this procedure, a thin tube with a camera is inserted through a small incision in the abdomen to directly visualize and confirm the presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus.

Treatment Options for Endometriosis
Treatment for endometriosis aims to alleviate symptoms, manage pain, and improve fertility. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and a woman’s future reproductive plans. Here are some common treatment options:
- Pain Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications may help manage pain and discomfort.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormonal treatments like birth control pills, hormone-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs), or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists can help regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce pain associated with endometriosis.
- Surgery: In cases of severe endometriosis or when fertility is a concern, surgical options include laparoscopic excision of endometrial tissue, ovarian cystectomy, or in more extreme cases, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus).
- Fertility Treatments: If endometriosis is causing infertility, fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended.
Conclusion
Endometriosis is a complex and often painful condition that can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life. Early diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. If you suspect you may have endometriosis or are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider who can provide a proper diagnosis and discuss treatment options tailored to your needs. Remember that with the right medical care and support, many women with endometriosis can lead fulfilling lives.













