Cholesterol is a type of fat that is found in the blood cells of the body. While it is essential for our body’s proper functioning, high levels of cholesterol can lead to various health problems, including heart disease. In this blog post, we will delve into the topic of understanding cholesterol and its impact on heart health.
Part 1: What is cholesterol and its types?
Cholesterol is a waxy substance that is produced in the liver and is also found in certain foods. There are two types of cholesterol, namely, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
LDL is often referred to as ‘bad cholesterol’ as it can build up in the arteries and form plaques, which can lead to heart disease. On the other hand, HDL is known as ‘good cholesterol’ as it helps remove LDL from the arteries and transport it to the liver, where it can be processed and eliminated from the body.
Part 2: Understanding the impact of high cholesterol on heart health:
High levels of LDL in the blood can lead to the accumulation of plaque in the arteries, which can narrow them and reduce blood flow to the heart. This can lead to various heart problems, including:
Coronary artery disease (CAD):
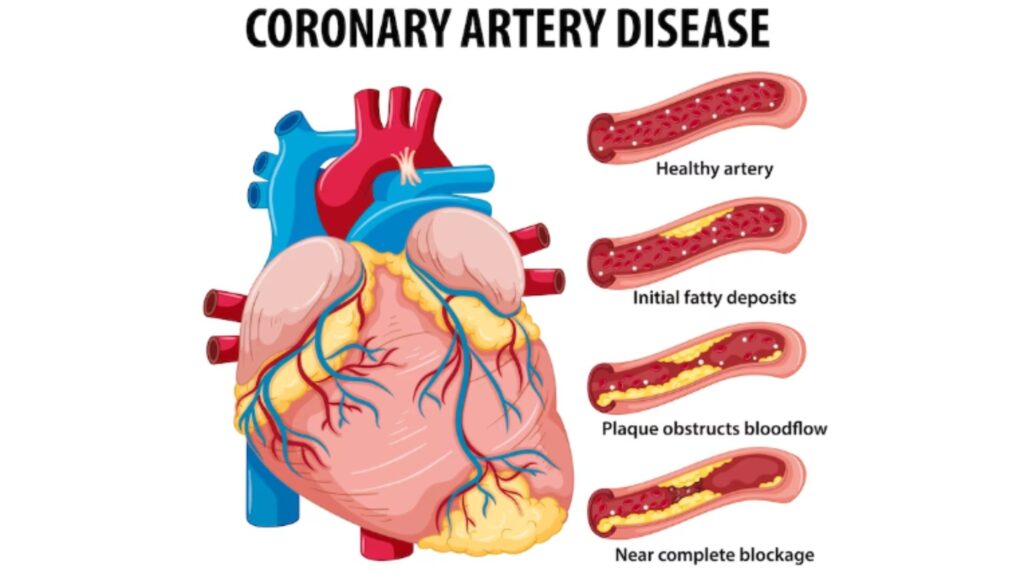
This occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup, which can lead to chest pain, heart attack, or stroke.
Peripheral artery disease (PAD):
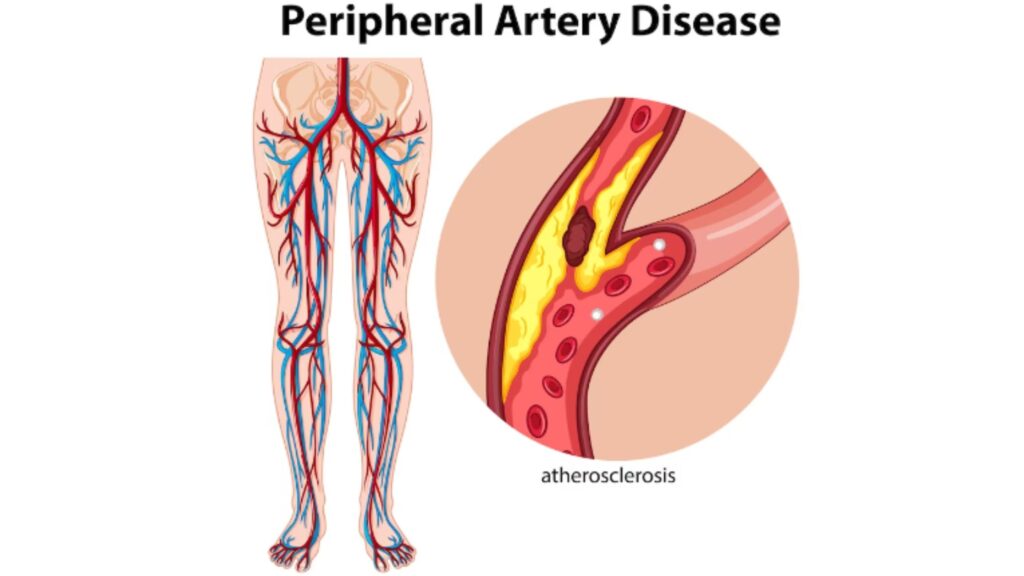
This occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the arms and legs become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup, which can lead to pain, numbness, or infections in the affected areas
Atherosclerosis:
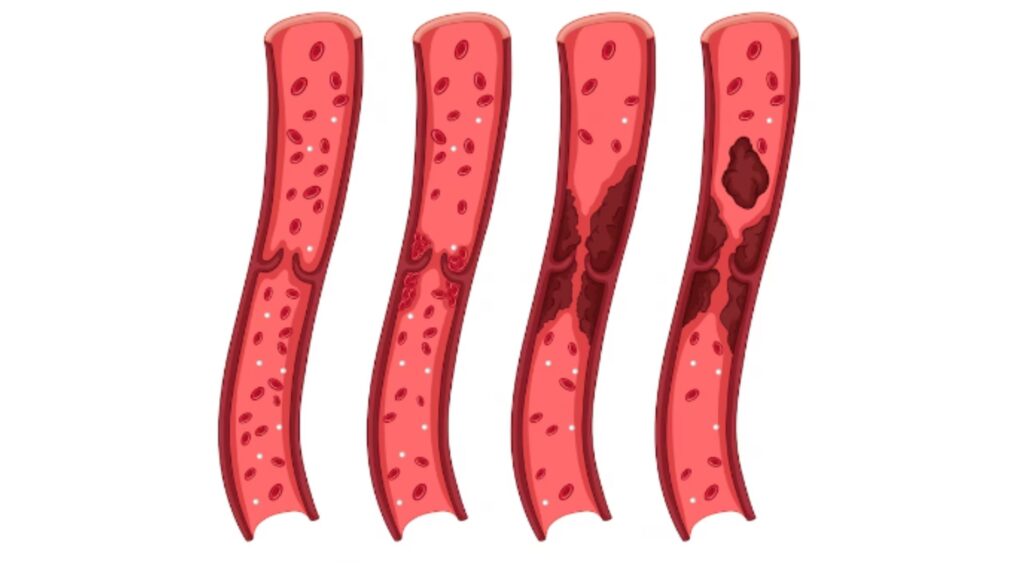
This is a condition in which plaque buildup occurs in the arteries throughout the body, leading to an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, or other cardiovascular diseases.
Part 3: Causes of high cholesterol:
High cholesterol can be caused by various factors, including:
- Unhealthy diet: A diet that is high in saturated and trans fats can increase LDL levels in the blood.
- Lack of physical activity: Regular exercise can help increase HDL levels and reduce LDL levels in the blood.
- Genetics: Some people are genetically predisposed to high cholesterol levels.
- Age and gender: As we age, our cholesterol levels tend to increase. Men are also more likely to have high cholesterol levels than women.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, and hypothyroidism can increase the risk of high cholesterol.
Part 4: Prevention and treatment of high cholesterol:
Preventing and treating high cholesterol involves various lifestyle changes and medications, including:
- Healthy diet: A diet that is low in saturated and trans fats and high in fiber, fruits, and vegetables can help reduce cholesterol levels.
- Regular exercise: Exercise can help increase HDL levels and reduce LDL levels in the blood.
- Medications: Statins and other cholesterol-lowering medications can help reduce cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking can increase LDL levels and decrease HDL levels in the blood, making it harder to manage cholesterol levels.
Part 5: Conclusion:
In conclusion, high cholesterol can have a significant impact on heart health and increase the risk of various cardiovascular diseases. Understanding the causes and risk factors of high cholesterol, as well as adopting healthy lifestyle changes and seeking medical treatment when necessary, can help reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall health.