Introduction
Jaundice is a condition that can affect individuals of all ages, from newborns to adults. It’s characterized by the yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eyes. While jaundice is a common condition, it can be a sign of underlying health issues. In this blog, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for jaundice to help you better understand this condition.
Causes of Jaundice
Jaundice occurs when there is a buildup of bilirubin in the body. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment produced during the natural breakdown of red blood cells. Several factors can contribute to increased bilirubin levels:
Hemolysis: Increased breakdown of red blood cells, often due to conditions like hemolytic anemia.
Liver Disorders: Liver diseases, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer, can impair the liver’s ability to process bilirubin.
Bile Duct Obstruction: Blocked bile ducts can prevent bilirubin from being excreted, leading to jaundice. This can be caused by gallstones, tumors, or inflammation.
Newborn Jaundice: Many newborns develop jaundice shortly after birth due to their immature liver function. This type of jaundice is usually temporary and resolves on its own.
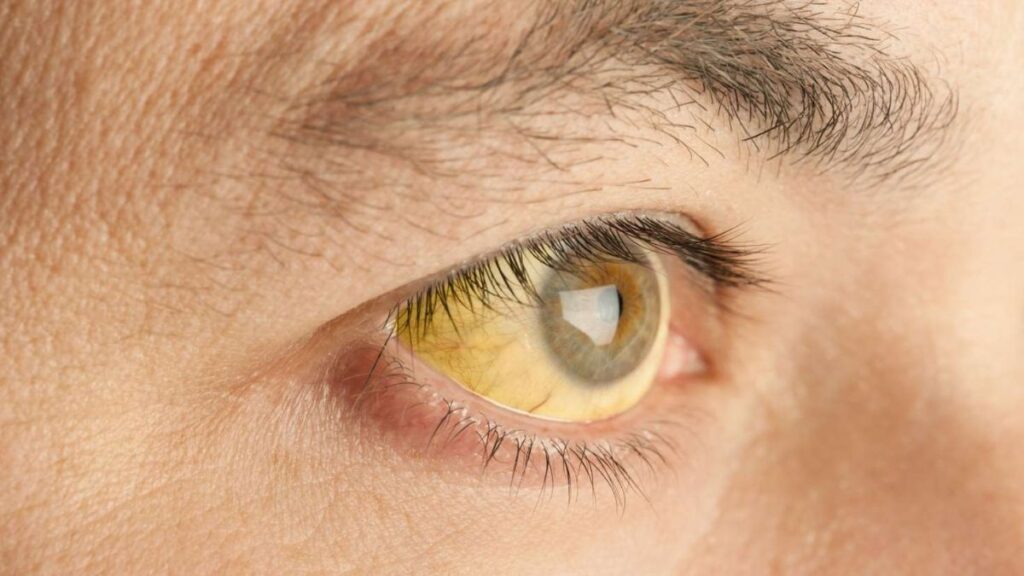
Symptoms of Jaundice
The most prominent symptom of jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and eyes. However, other symptoms may accompany it, depending on the underlying cause:
Yellow Skin and Eyes: The hallmark sign of jaundice.
Pale Stools: Bilirubin gives stool its normal brown color. In jaundice, stools may become pale or clay-colored.
Dark Urine: High bilirubin levels can lead to dark, tea-colored urine.
Fatigue: Individuals with jaundice may experience fatigue and weakness.
Abdominal Pain: In cases of gallstones or liver disease, abdominal pain may be present.
Itching: Accumulation of bilirubin in the skin can cause itching.
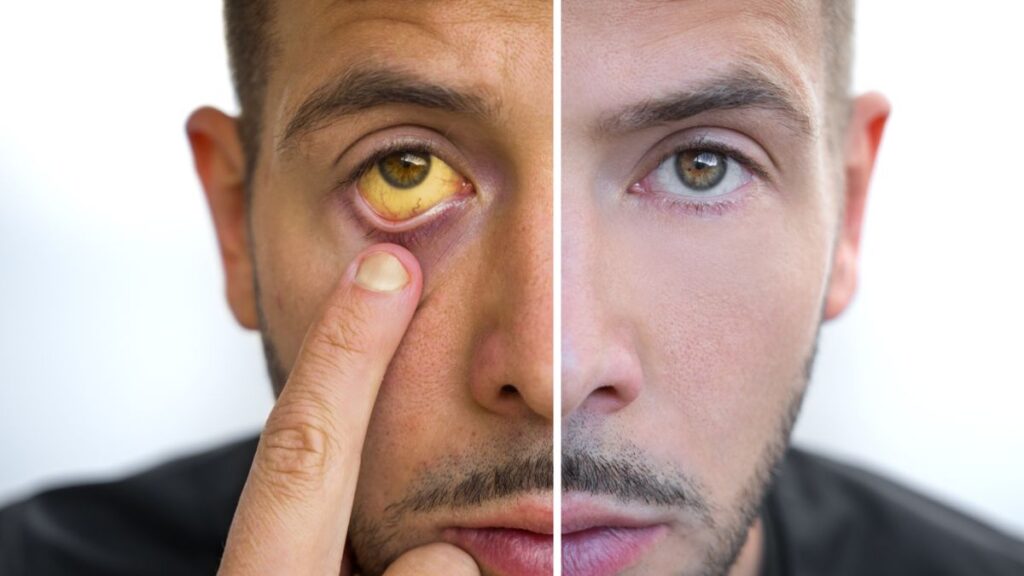
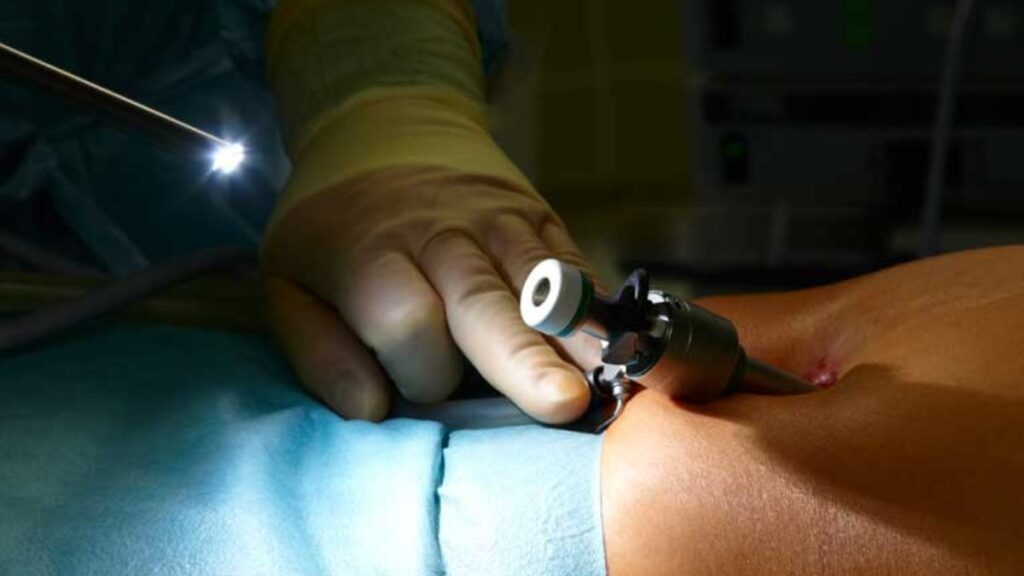
Diagnosis and Treatment
To determine the cause of jaundice, healthcare providers will perform a thorough evaluation, including blood tests, imaging scans (such as ultrasound or MRI), and sometimes a liver biopsy.
Treatment for jaundice depends on its underlying cause:
Managing Underlying Conditions: If jaundice is due to an underlying condition like hepatitis or cirrhosis, treatment will focus on managing and treating that condition.
Removing Obstructions: If bile ducts are blocked, procedures or surgery may be needed to remove the obstruction.
Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to reduce bilirubin levels or manage symptoms.
Phototherapy: Newborns with jaundice may be treated with phototherapy, a light therapy that helps break down bilirubin in the skin.
Lifestyle Changes: Individuals with jaundice, particularly due to liver disease, may need to make dietary and lifestyle changes to support liver function.
Conclusion
Jaundice is a symptom of an underlying problem rather than a disease itself. It’s essential to seek medical attention if you or a loved one experiences symptoms of jaundice. Early diagnosis and treatment can help address the underlying cause and prevent potential complications. Remember, jaundice can be a sign of various medical conditions, so a thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider is crucial for effective management and a healthier life.